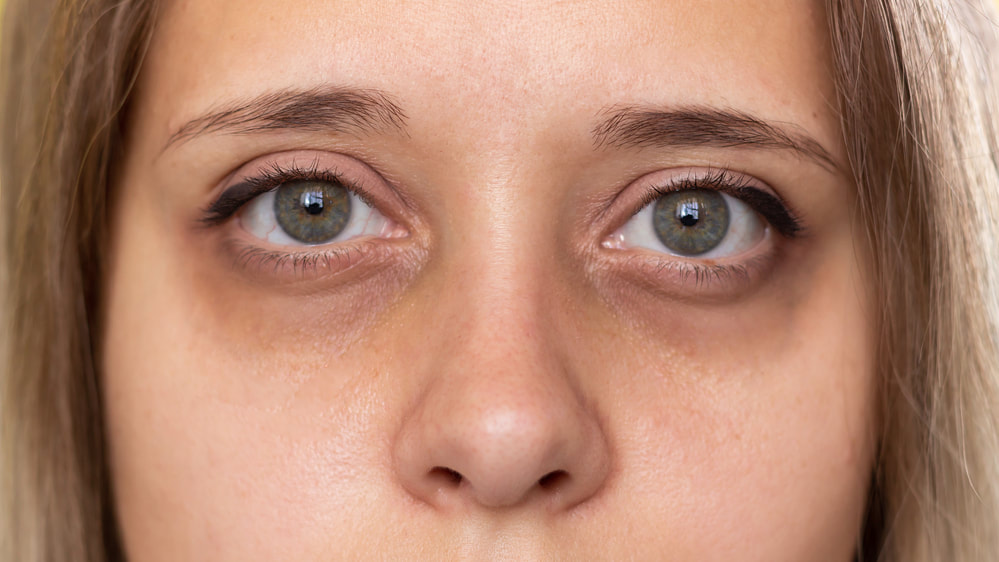
How does sleep affect the eyes?When we sleep, our bodies recharge and heal. Not getting enough sleep can affect how well your eyes heal from the everyday effects of eye strain and environmental factors, such as dry air, allergens, and pollutants. For example, some studies show an increased risk of developing dry eyes in people that do not get adequate rest. A study in the journal The Ocular Surface involved 71,761 adults from ages 19 to 94. The participants were assessed for dry eyes and also completed a sleep quality index. A total of 8.9 percent of people in the study had dry eyes. Of those, 36.4 percent had poor sleep as compared to 24.8 percent that reported good sleep. Certain sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea, may affect how much oxygen gets to the retina. Sleep apnea involves short pauses in breathing due to airway obstruction. Those brief pauses may cause oxygen levels to drop. Over time, untreated sleep apnea can lead to an increased risk of high blood pressure and a stroke, which also can affect vision. Eye and vision issues related to poor sleepPoor sleep can have various effects on the eyes. Many of the effects are cosmetic and are corrected with a good night’s sleep. For instance, if you are short on sleep, you might notice bloodshot eyes and eye bags. Not getting enough rest may also leave your eyes feeling tired and sensitive to light. Some people also experience eye twitching when they are sleep-deprived. The reason for increased eye twitching is not clear, but it does appear to be associated with a lack of sleep. Although many of the eye effects linked to poor sleep are minor, one serious consequence may also occur. According to the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, having sleep apnea is a risk factor for developing glaucoma. Glaucoma involves an eye condition that can lead to damage to the optic nerve and potentially vision loss. The reason sleep apnea is linked to an increased risk of glaucoma is not clear, but it may be due to decreased oxygen levels in the body from apnea. How much sleep do we need?The amount of sleep a person needs depends on several factors. There is no one size fits all. The amount of sleep you need may depend on your age, health, and how active you are. In general, most experts recommend between seven and nine hours of sleep each night. If you are not getting enough sleep, consider some of the tips below for better sleep. Better sleep tipsThere are several things you can do to increase the quantity and quality of your sleep, such as the following:
Treat underlying sleep disorders: If you think you have a sleep disorder, such as apnea, talk with your doctor. Treatment, such as CPAP, can reduce your risk of complications. Develop a schedule: Waking and sleeping at the same time each day helps you develop an internal rhythm and improve the quality of your sleep. Limit caffeine: Caffeine can interfere with both falling and staying asleep. Limit caffeine several hours before bedtime. Get regular exercise: Exercise can help improve your overall quality of sleep. Just don’t do a vigorous workout too close to bedtime. Reduce screen time before bed: Too much screen time before bed stimulates your brain. Turn off the computer, tablet, and cellphone a few hours before hitting the sack. We hope the tips above help you sleep well and keep your eyes healthy. If you have any questions or concerns, we are happy to help. Also, if you would like to ask whether an appointment with one of our eye doctors would be appropriate at this time, call our office at 508-746-8600. Comments are closed.
|
EYE HEALTH BLOGCategories
All
Archives
July 2024
|
|
Kadrmas Eye Care New England
55 Commerce Way, Plymouth, MA 02360
14 Tobey Road, Wareham, MA 02571 133 Falmouth Road (Rt 28), Mashpee, MA 02649 |
Phone Number:
1-508-746-8600 Hours: Monday through Friday — 8 AM – 4:30 PM |

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
